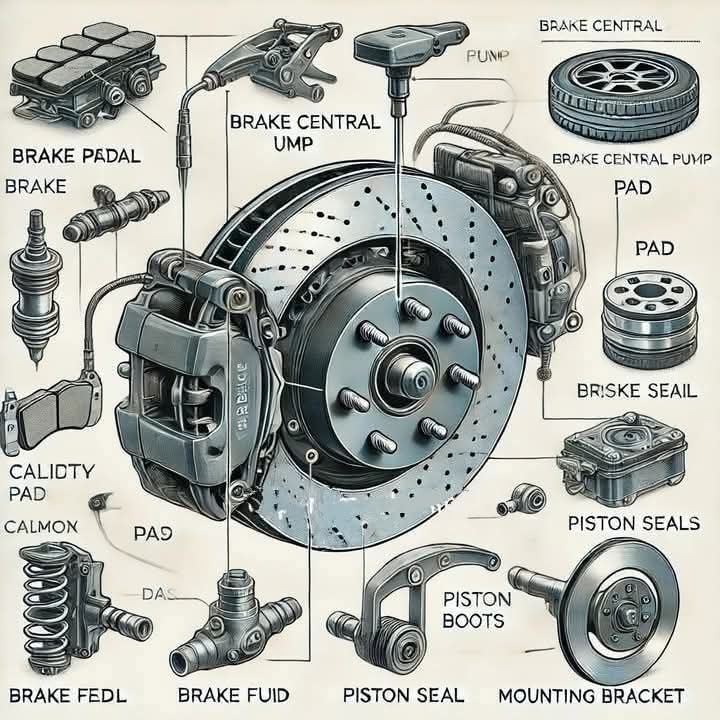
a brake system, likely for a car. Here's a breakdown of the labeled components:
Main Components:
* Brake Pedal: The driver applies pressure to this pedal to initiate braking.
* Brake Central Pump: This is the heart of the hydraulic braking system. It converts the mechanical pressure from the pedal into hydraulic pressure.
* Brake Pad: These friction pads are mounted on the caliper and press against the brake rotor to slow down the vehicle.
* Brake Rotor: A metal disc that rotates with the wheel. The brake pads clamp onto it to create friction and slow down the wheel.
* Caliper: A housing that holds the brake pads and applies pressure to them against the rotor.
* Piston: Located within the caliper, these push the brake pads against the rotor when hydraulic pressure is applied.
* Piston Seals: These prevent brake fluid from leaking past the piston.
* Piston Boots: These protect the piston seals from dirt and debris.
* Brake Fluid: This incompressible fluid transmits pressure from the master cylinder to the calipers.
* Brake Field: This likely refers to the area where the brake system operates, such as the wheels or the brake lines.
* Mounting Bracket: This attaches the caliper to the vehicle's suspension.
Other Components:
* Brisk Seal: This is likely a type of seal used in the brake system.
* Calidity Calmon: This might refer to a type of brake pad material or a brand.
Overall, the image provides a comprehensive view of the key components involved in a typical hydraulic brake system and how they work together to slow down and stop a vehicle.
#automotive #mechaniclife #cars #mechanical #mechanic #carparts #restoration #viral #carmemes #usa
#fypシ #autos #automobile #mechanic #mechanical #engineering #cars #engine #sensors #usa #australia
Main Components:
* Brake Pedal: The driver applies pressure to this pedal to initiate braking.
* Brake Central Pump: This is the heart of the hydraulic braking system. It converts the mechanical pressure from the pedal into hydraulic pressure.
* Brake Pad: These friction pads are mounted on the caliper and press against the brake rotor to slow down the vehicle.
* Brake Rotor: A metal disc that rotates with the wheel. The brake pads clamp onto it to create friction and slow down the wheel.
* Caliper: A housing that holds the brake pads and applies pressure to them against the rotor.
* Piston: Located within the caliper, these push the brake pads against the rotor when hydraulic pressure is applied.
* Piston Seals: These prevent brake fluid from leaking past the piston.
* Piston Boots: These protect the piston seals from dirt and debris.
* Brake Fluid: This incompressible fluid transmits pressure from the master cylinder to the calipers.
* Brake Field: This likely refers to the area where the brake system operates, such as the wheels or the brake lines.
* Mounting Bracket: This attaches the caliper to the vehicle's suspension.
Other Components:
* Brisk Seal: This is likely a type of seal used in the brake system.
* Calidity Calmon: This might refer to a type of brake pad material or a brand.
Overall, the image provides a comprehensive view of the key components involved in a typical hydraulic brake system and how they work together to slow down and stop a vehicle.
#automotive #mechaniclife #cars #mechanical #mechanic #carparts #restoration #viral #carmemes #usa
#fypシ #autos #automobile #mechanic #mechanical #engineering #cars #engine #sensors #usa #australia
a brake system, likely for a car. Here's a breakdown of the labeled components:
Main Components:
* Brake Pedal: The driver applies pressure to this pedal to initiate braking.
* Brake Central Pump: This is the heart of the hydraulic braking system. It converts the mechanical pressure from the pedal into hydraulic pressure.
* Brake Pad: These friction pads are mounted on the caliper and press against the brake rotor to slow down the vehicle.
* Brake Rotor: A metal disc that rotates with the wheel. The brake pads clamp onto it to create friction and slow down the wheel.
* Caliper: A housing that holds the brake pads and applies pressure to them against the rotor.
* Piston: Located within the caliper, these push the brake pads against the rotor when hydraulic pressure is applied.
* Piston Seals: These prevent brake fluid from leaking past the piston.
* Piston Boots: These protect the piston seals from dirt and debris.
* Brake Fluid: This incompressible fluid transmits pressure from the master cylinder to the calipers.
* Brake Field: This likely refers to the area where the brake system operates, such as the wheels or the brake lines.
* Mounting Bracket: This attaches the caliper to the vehicle's suspension.
Other Components:
* Brisk Seal: This is likely a type of seal used in the brake system.
* Calidity Calmon: This might refer to a type of brake pad material or a brand.
Overall, the image provides a comprehensive view of the key components involved in a typical hydraulic brake system and how they work together to slow down and stop a vehicle.
#automotive #mechaniclife #cars #mechanical #mechanic #carparts #restoration #viral #carmemes #usa
#fypシ #autos #automobile #mechanic #mechanical #engineering #cars #engine #sensors #usa #australia
0 Comments
0 Shares